Net Present Value NPV: What It Means and Steps to Calculate It
Instead, they must be translated into a common time period using time value of money techniques. By converting all of the cash flows that will occur from a project into present value, or current dollars, the cash inflows from the project can be compared to the cash outflows. If the cash inflows exceed the cash outflows in present value terms, the project will add value and should be accepted. The difference between the present value of the cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows is known as net present value (NPV). They react to changes in input variables—be it cash flows, discount rates, or project timelines. Sensitivity analysis, often conducted alongside NPV profiling, sheds light on the robustness of investment decisions.
Net Present Value Profile: How to Plot the Net Present Value Profile of Your Projects
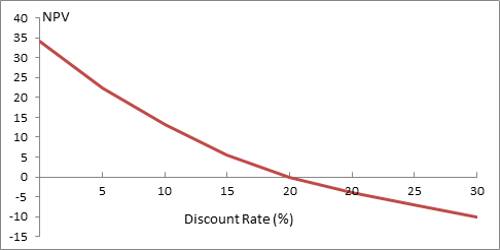
This project has six future cash flows, so six present values must be computed. The NPV Profile is a graphical illustration of a project’s NPV graphed as a function of various discount rates. The NPV values are graphed on the vertical or y-axis while the discount rates are graphed on the horizontal or x-axis. When faced with multiple investment opportunities, decision-makers can employ NPV profiles to rank projects.
The Cost of Capital
It is essentially the difference between the present value of cash flows and the initial investment based on the discount rate. The discount rate is mainly decided on the basis of the debt and equity mix used to finance the investment and to pay for the debt. It also incorporates the risk factor, which is inherent in the investment.
What is your current financial priority?
As a result, projects or investments become less attractive because their potential profitability appears diminished when evaluated against a higher required rate of return. Net Present Value (NPV) is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment or project. It takes into account the time value of money, which means that a dollar received in the future is worth less than a dollar received today. By discounting future cash flows to their present value, NPV helps determine whether an investment is worthwhile. The net present value mainly measures the net increase in the company’s equity by working on a project.
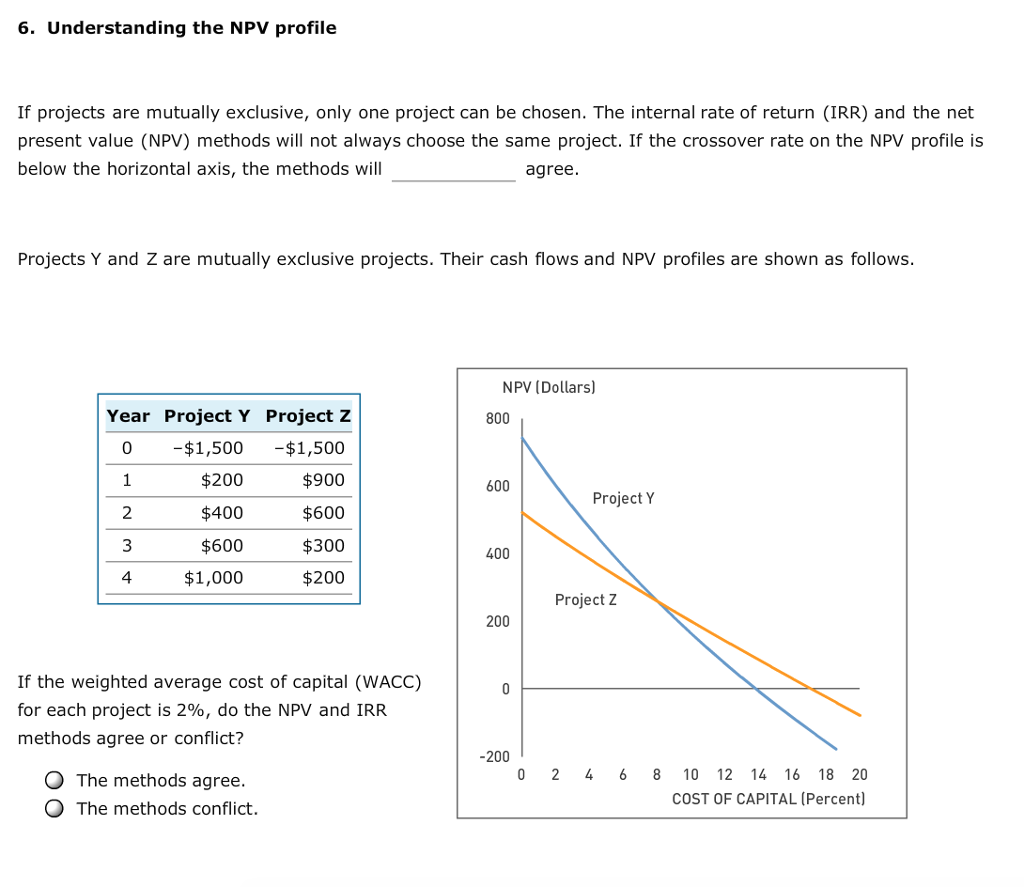
Remember, npv sensitivity analysis isn’t about predicting the future with certainty; it’s about understanding the range of possible outcomes. By considering these key variables, you’ll be what are the different types of accountants better equipped to make strategic investment decisions. Looking at the different NPV (Net Present Value) profile values, it is conveyed that Project A performs better at 18.92% and 20%.
Facilitates Comparison of Investment Alternatives
Capital rationing becomes a strategic exercise, where projects compete for limited funds. In the realm of investment analysis, the Net Present Value (NPV) profile stands as a powerful tool that transcends mere numerical calculations. It is more than just a financial metric; it is a compass guiding decision-makers through the intricate landscape of investment projects. As we delve into the depths of this topic, let us explore the multifaceted facets of NPV profiles and their implications. It empowers decision-makers to navigate the complex landscape of investments, combining financial rigor with strategic vision.
- Remember, the NPV profile isn’t just a static graph; it’s a dynamic tool that informs strategic decisions.
- If the company borrows all the money for the project — for example, by issuing bonds — the cost of capital would be the after-tax interest it pays on the bonds plus any issuance costs.
- Because the cash inflows and outflows occur in different time periods, they cannot be directly compared to each other.
- It calculates the present value of future cash flows by discounting them back to the present using a specified discount rate.
NPV is an important tool in financial decision-making because it helps to determine whether a project or investment will generate a positive or negative return. If the NPV is positive, it indicates that the investment is expected to generate more cash flows than the initial investment and is therefore a good investment. If the NPV is negative, it indicates that the investment is not expected to generate enough cash flows to cover the initial investment and is therefore a bad investment. The NPV profile also allows for sensitivity analysis by examining how changes in key variables impact the project’s profitability.
While some prefer using IRR as a measure of capital budgeting, it does come with problems because it doesn’t take into account changing factors such as different discount rates. The payback period is the time required for an investment or project to recoup its initial costs. Shorter payback periods are generally more attractive, as they indicate faster recovery of the initial investment. The internal rate of return (IRR) is calculated by solving the NPV formula for the discount rate required to make NPV equal zero. This method can be used to compare projects of different time spans on the basis of their projected return rates. In summary, the NPV profile graph provides a visual roadmap for decision-makers.
The calculation could be more complicated if the equipment were expected to have any value left at the end of its life, but in this example, it is assumed to be worthless. Imagine a company can invest in equipment that would cost $1 million and is expected to generate $25,000 a month in revenue for five years. Alternatively, the company could invest that money in securities with an expected annual return of 8%. Management views the equipment and securities as comparable investment risks.
If the cost of capital is more than 14%, however, the NPV is negative, and the company should reject the project. The NPV profile is a graphical representation of the net present value (NPV) of an investment project at different discount rates. It helps in assessing the sensitivity of the project’s profitability to changes in the discount rate. By plotting the NPV against different discount rates, we can gain insights into the project’s risk and return characteristics.

